Why Is My WiFi Signal So Weak in Certain Rooms?

WiFi signal strength relates to your device’s ability to connect and maintain a connection to your wireless router. It is measured in dBm (decibels milliwatts) and is an important component of everything from browsing speed to video streaming and gaming quality. When you have a strong signal strength, your connection should be fast and stable, while a weak signal strength leads to buffering, lag, and a bad experience. Knowing how a signal works and how to test signal strength and improve it can limit areas of weak connection (dead zones) so they become areas of reliable connection throughout your home.
What Causes Weak WiFi Signal Strength in Certain Rooms?
Most people think that WiFi signal strength should be the same throughout their house, and many are surprised when it is often affected by multiple environmental and physical factors that will impact every wireless signal. Here is a look at what may be making your WiFi signal stronger or weaker in certain rooms:
1. Distance from the Router
WiFi signals weaken the farther they travel. If your device is far from the router, especially on a different floor or across the house, you are likely to experience a noticeable drop in signal.
2. Wall Materials and Obstructions
Some walls are worse than others when it comes to blocking WiFi. Concrete, brick, metal, and even some thick wooden walls can degrade the WiFi signal strength significantly. Mirrors and large furniture can also reflect or absorb signals.
3. Interference from Other Devices
Microwaves, baby monitors, cordless phones, and even neighboring WiFi networks can cause interference. These signals often overlap, especially on the crowded 2.4 GHz frequency.
4. Router Placement
Placing your router on the floor, in a cabinet, or near heavy appliances can block or scatter your signal. A poorly placed router is one of the top causes of weak WiFi signal strength in certain areas.
5. Outdated Equipment
Older routers may not have the range, power, or bandwidth management that newer models provide. If your router is over 5 years old, it may be time for an upgrade.
How to Check WiFi Signal Strength in Every Room
Before you can fix a weak connection, you need to measure your WiFi strength in different areas of your home. Luckily, this is simple and doesn’t require any technical knowledge.
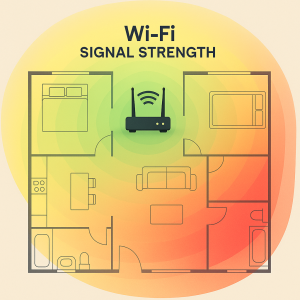
WiFi Signal Heatmap: What the Colors Mean
In the heatmap image, different colors represent the strength of the WiFi signal throughout a home. Here’s how to interpret each zone:
🟢 Green Zone – Strong Signal (-30 to –50 dBm)
-
Closest to the router
-
Best for high-speed activities: HD streaming, online gaming, video calls
-
Very stable connection with minimal dropouts
🟡 Yellow Zone – Moderate Signal (-51 to –67 dBm)
-
A little further from the router or partially blocked by walls/furniture
-
Suitable for web browsing, emails, and moderate streaming
-
May start to show slower speeds if multiple devices are connected
🔴 Red Zone – Weak Signal (-68 dBm and below)
-
Farthest from the router or heavily obstructed (thick walls, doors, appliances)
-
Commonly found in corners, basements, or far rooms
-
Results in slow speeds, buffering, or connection drops
-
Ideal candidate areas for WiFi extenders or mesh nodes
What Is a Good WiFi Signal Strength?
WiFi signal is measured in decibels relative to a milliwatt (dBm). Here’s a quick reference:
| Signal Strength (dBm) | Quality |
|
-30 to -50 dBm |
Excellent |
|
-51 to -67 dBm |
Good |
| -68 to -70 dBm |
Fair |
| -71 to -90 dBm |
Weak/Poor |
The closer the number is to 0, the stronger the signal.
WiFi Signal Strength App and Meter Tools
To test your signal, use a WiFi signal strength meter or app on your smartphone or laptop. These tools help you walk around your home and pinpoint weak spots.
Recommended WiFi Signal Strength Apps:
- NetSpot (Windows, macOS): Great for generating heatmaps of your signal throughout the home.
- WiFi Analyzer (Android): Simple graphs and channel visualization.
- AirPort Utility (iOS): A lesser-known tool built into iPhones and iPads.
- WiFi Signal Strength Meter Apps: Many third-party apps show real-time signal in dBm.
You don’t have to be a tech expert—just walk around your home with one of these apps open and watch how the signal changes room by room.
Use Our WiFi Signal Strength Test Online Tool
Want a faster way to test your connection without installing an app? Try the free WiFi signal strength test online at DNA Goa.
With just one click, you can:
- Check your download and upload speed
- See how stable your signal is
- Identify if the problem is due to weak WiFi signal strength
This tool is perfect for users who want a quick snapshot of their current performance, especially before jumping into more advanced solutions.
How to Improve WiFi Signal Strength in Weak Rooms
Once you’ve measured your signal and identified weak zones, here are the most effective ways to boost your WiFi signal strength:
1. Move Your Router to a Better Location
Position your router in a central, open area, preferably raised (like on a shelf) and away from walls or metal furniture. Avoid hiding it in closets or near large electronics.
2. Switch to 5 GHz or Dual-Band Mode
Most modern routers support 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. The 5 GHz band is faster but has a shorter range, while 2.4 GHz travels farther but is slower. Dual-band routers automatically switch between them for the best performance.
3. Use a Mesh WiFi System
Mesh systems like Google Nest WiFi or TP-Link Deco place small access points around your home that communicate with each other. These are great for eliminating weak signal rooms and large spaces.
4. Add a WiFi Range Extender
If a mesh system feels like overkill, a range extender can be a more affordable solution. Just plug it into a wall outlet between your router and the problem area.
5. Upgrade Your Router
If you’re still using the same router you bought in 2015, it’s time for an upgrade. Look for one with:
- At least dual-band support
- Beamforming technology
- MU-MIMO (for handling multiple devices at once)
6. Use Wired Connections Where Possible
For smart TVs or gaming consoles in weak signal areas, consider using Ethernet over Powerline adapters. These send internet signals through your home’s electrical wiring.
Pro Tips for Boosting WiFi Signal Strength in Specific Situations
-
For Apartments:
Use 5 GHz to reduce interference from neighbors, and check for channel overlap using apps like WiFi Analyzer.
-
For Multi-Story Homes:
Place your router on the middle floor and use mesh satellites on each level.
-
For Outdoor Areas:
Invest in an outdoor-rated access point or extender to bring strong signal strength WiFi to your garden or patio.
Troubleshooting Common WiFi Signal Strength Problems
Problem: WiFi works fine in one room but is terrible in another
Fix: Reposition the router or use a mesh extender in the weak area.
Problem: Signal is strong, but speed is slow
Fix: Test your internet speed using DNA Goa’s tool , the issue might be with your internet provider, not your WiFi.
Problem: WiFi drops when using the microwave or a cordless phone
Fix: Switch devices to 5 GHz and move the router away from those appliances.
Final Thoughts: Take Control of Your WiFi Signal Strength
Weak WiFi signal strength in certain rooms isn’t something you have to live with. Now that you know how to measure it using a WiFi signal strength meter, a signal test app, or our free online tool, you can pinpoint the problem and take action.
Simple steps like moving your router, upgrading your gear, or using a mesh system can turn frustrating “dead zones” into strong, stable connection areas.
Quick Checklist to Boost Your WiFi Signal Strength
- Use a WiFi signal strength app to test your
- Check the signal in each room with DNA Goa’s test
- Reposition or upgrade your
- Consider a mesh system or extender
- Switch to 5 GHz or adjust router channels
FAQ for WiFi signal strength
Q: How do I check my Wi-Fi signal strength?
A: You can check your Wi-Fi signal strength using the built-in Wi-Fi icon on your device (more bars = stronger signal), or for a more accurate reading, use a Wi-Fi signal strength meter app like NetSpot, WiFi Analyzer, or AirPort Utility. For a quick, no-download option, use the WiFi Signal Strength Test Online by DNA Goa to instantly measure your signal.
Q: Is 100% signal strength good?
A: Yes, 100% signal strength usually means an excellent connection with minimal interference and maximum speed. However, high signal strength doesn’t always guarantee performance; network congestion or slow internet plans can still affect your experience.
Q: What is normal signal strength?
A: Normal WiFi strength typically falls between -30 dBm and -67 dBm. This range is considered strong enough for most online activities like browsing, streaming, video calls, and gaming.
 0832-6747575
0832-6747575









