Why Internet Speed Isn’t Everything: The Role of Latency and Bandwidth

When people evaluate an internet plan, they often focus on speed, which is usually measured in megabits per second (Mbps) or gigabits per second (Gbps). Speed is just one component. Two other significant components, latency and bandwidth, play a decisive role in defining your experience. By understanding these, you are more likely to make informed decisions and troubleshoot faster and more effectively.
Latency and bandwidth might sound a little technical, but these two concepts are important to understanding why your video call freezes or the game you are playing lags, even though your internet plan is “lightning-fast.” Let’s break it down into plain language.
What is Bandwidth?

Bandwidth is the maximum amount of data you can transmit over your internet connection over a given time period. You can think about bandwidth in terms of width on a highway. The wider the highway, the more cars can travel at the same time.
If you are streaming Netflix using 4k, if you are downloading files, and contributing to a video call, you need your connection to have enough bandwidth to sustain all of those data transfers. If your pipe (bandwidth) is too narrow, everything slows down.
- High bandwidth allows more data to flow, which is beneficial for activities like streaming high-definition videos or downloading large files.
- Low bandwidth can lead to congestion, especially if multiple devices are connected and using the internet simultaneously.
Every day examples of high bandwidth needs:
- Streaming 4K video
- Large file downloads
- Backing up data to the cloud
- Running smart home devices on the same network
It is important to note that bandwidth represents potential capacity. Just because you have a high-bandwidth connection doesn’t guarantee that all your data will flow smoothly; other factors come into play.
Work. Stream. Game. Without Limits.
Experience uninterrupted internet with DNA Goa.
What is Latency?

Latency is the time it takes for data to travel from its source to its destination. It’s often measured in milliseconds (ms). Continuing with the highway analogy, latency is like the time it takes for a car to travel from one city to another.
- Low latency means data travels quickly, resulting in a more responsive experience.
- High latency can cause delays, leading to issues like lag in online games or buffering during video calls.
Activities that need low latency:
- Online gaming
- Video conferencing
- Voice over IP (VoIP) calls
- Remote work apps like Zoom or Teams
Even if you have tons of bandwidth, high latency can ruin these experiences. That’s why gamers care more about “ping” (a measure of latency) than raw speed.
Real-World Scenarios: How This Plays Out?
Scenario 1: High Bandwidth, High Latency
You’re on a satellite internet connection with a 100 Mbps download speed. But because the signal travels to space and back, your latency is over 600 ms. Result? Fast downloads, but terrible lag in Zoom meetings and online games.
Scenario 2: Low Bandwidth, Low Latency
You’re on a 10 Mbps fiber connection with 15 ms latency. Web pages load fast, and Zoom calls are crisp, but you can’t stream 4K or download large files quickly. Great for responsiveness, not for heavy media.
Scenario 3: Balanced Connection
You’re on a 100 Mbps fiber line with 20 ms latency. Smooth video calls, fast downloads, and lag-free gaming. This is the sweet spot most users aim for.
Bandwidth vs. Latency vs. Throughput: Key Differences
Here’s a simple table to show the differences:
|
Term |
What It Means | Unit | Affects | Example |
|
Bandwidth |
Max data that can pass through | Mbps/Gbps | Capacity | Number of users or HD streams |
|
Latency |
Time delay in sending/receiving data | Milliseconds | Speed |
Gaming lag, call delay |
| Throughput | Actual data transferred per second | Mbps | Efficiency |
Real-world performance |
Upgrade to Faster Speeds Today
Boost your connection with our fiber-powered internet plans
Why Speed Tests Can Be Misleading
Most people run a speed test and see a number like 100 Mbps and assume everything should work perfectly. But that number only shows bandwidth, not latency or throughput.
Here’s why that’s a problem:
- Your connection could be 100 Mbps with high latency, causing choppy video calls.
- Speed tests often measure download speed, not how fast data comes back and forth (which affects real-time use).
So while speed tests are helpful, they don’t show the full picture.
Factors Affecting Latency
Several factors can contribute to increased latency:
- Physical Distance: Data traveling over long distances takes more time, increasing latency.
- Network Congestion: High traffic can slow down data transmission.
- Routing Paths: Inefficient routing can add delays.
- Hardware Limitations: Older or low-quality equipment can process data more slowly.
- Bufferbloat: Excessive buffering in network devices can cause high latency and jitter.
Visual: Latency vs Bandwidth Impact on Common Activities
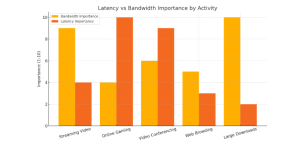
Here is a comparison chart showing how Latency and Bandwidth affect different internet activities. As you can see:
- Online gaming and video conferencing depend heavily on low latency.
- Streaming and downloads require high bandwidth more than low latency.
- Web browsing sits somewhere in the middle.
Real-World Impacts
Understanding how bandwidth and latency affect different activities can help you optimize your internet usage:
- Streaming Video: Requires sufficient bandwidth to handle the data load. High latency can cause buffering.
- Online Gaming: Needs low latency for real-time responsiveness. Bandwidth requirements are moderate.
- Video Conferencing: Demands both adequate bandwidth and low latency to maintain quality and synchronization.
- Web Browsing: Generally tolerant of higher latency but benefits from higher bandwidth for loading media-rich pages.
Tips to Improve Your Internet Experience
- Upgrade Equipment: Use modern routers and modems that can handle higher speeds and manage traffic efficiently.
- Optimize Placement: Position your router centrally to ensure even coverage.
- Limit Interference: Keep the router away from devices that can cause signal interference.
- Manage Connected Devices: Too many devices can strain bandwidth; disconnect those not in use.
- Use Wired Connections: Ethernet connections offer lower latency compared to Wi-Fi.
- Regularly Update Firmware: Ensure your network devices have the latest updates for optimal performance.
- Monitor Network Usage: Use tools to identify bandwidth hogs and manage them accordingly.
Conclusion
While internet speed is often the headline feature of any internet plan, it’s essential to understand that Latency and Bandwidth are equally important in determining your online experience.
Both Latency and Bandwidth shape how your internet feels in real life. You can have the fastest connection on paper, but if your latency is high, you’ll feel the lag.
High bandwidth allows more data to flow, but without low latency, activities that require real-time interaction can suffer. By recognizing the roles of these factors and taking steps to optimize them, you can ensure a smoother and more efficient internet experience.
 0832-6747575
0832-6747575










